Complete about Oracle Parallelism?
Solution:
Following initialization parameters are required for parallelism setup in database.
PARALLEL_SERVER,
PARALLEL_SERVER_INSTANCES,
PARALLEL_MIN_SERVERS,
PARALLEL_MAX_SERVERS?
PARALLEL_THREADS_PER_CPU
Parallel Queries and Parallel jobs execution
1. Select query with parallelism example:
Select /*+ parallel (a,32) */ * from dba_segments a;
32 is degreee here(Numbers of parallel processes)
Gather statistics of a table using parallelism Example
exec FND_STATS.GATHER_TABLE_STATS (ownname => '&owner', tabname => '&table_name', percent => 20 ,degree => 30 , granularity => 'ALL', cascade => TRUE);
Comple objects in the database with parallelism Example
exec sys.utl_recomp.recomp_parallel(32);
Table used to know number of parallel processes running are
v$px_session - Standard
gv$px_session - For RAC
Sharing real time knowledge,issues on Oracle Apps DBA and Oracle DBA
Showing posts with label Oracle DBA - Interview Questions. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Oracle DBA - Interview Questions. Show all posts
Wednesday, January 14, 2009
Difference between DROP,Truncate and Delete in Oracle?
Difference between Truncate and Delete in Oracle?
Answer:
1.TRUNCATE is a DDL command and cannot be rolled back. All of the memory space is released back to the server.
2. DELETE is a DML command and can be rolled back.
3. TRUNCATE : You can't use WHERE clause and DELETE : You can use WHERE clause
4. Both commands accomplish identical tasks (removing all data from a table), but TRUNCATE is much faster.
5.Truncate: Drop all object's statistics and marks like High Water Mark, free extents and leave the object really empty with the first extent.Delete: You can keep object's statistics and all allocated space.
6. In case of TRUNCATE ,Trigger doesn't get fired.But in DML commands like DELETE .Trigger get fired.
7. Drop command will delete the entire row also the structure.But truncate will delete the contenets only not the strucure, so no need to give specifications for another table creation.
8. Drop command remove the table from data dictionary. This is the DDL statement. We can not recover the table before Oracle 10g. But Oracle 10g provide the command to recover it by using the command (FLASHBACK)
9. DROP and TRUNCATE are DDL commands, whereas DELETE is a DML command. Therefore DELETE operations can be rolled back (undone), while DROP and TRUNCATE operations cannot be rolled back.
From Oracle 10g a table can be "undropped". Example:
SQL> FLASHBACK TABLE emp TO BEFORE DROP;
Flashback complete.
PS: DELETE will not free up used space within a table. This means that repeated DELETE commands will severely fragment the table and queries will have to navigate this "free space" in order to retrieve rows.
10. Truncate will not use the undo TBS, whereas a delete will.
Answer:
1.TRUNCATE is a DDL command and cannot be rolled back. All of the memory space is released back to the server.
2. DELETE is a DML command and can be rolled back.
3. TRUNCATE : You can't use WHERE clause and DELETE : You can use WHERE clause
4. Both commands accomplish identical tasks (removing all data from a table), but TRUNCATE is much faster.
5.Truncate: Drop all object's statistics and marks like High Water Mark, free extents and leave the object really empty with the first extent.Delete: You can keep object's statistics and all allocated space.
6. In case of TRUNCATE ,Trigger doesn't get fired.But in DML commands like DELETE .Trigger get fired.
7. Drop command will delete the entire row also the structure.But truncate will delete the contenets only not the strucure, so no need to give specifications for another table creation.
8. Drop command remove the table from data dictionary. This is the DDL statement. We can not recover the table before Oracle 10g. But Oracle 10g provide the command to recover it by using the command (FLASHBACK)
9. DROP and TRUNCATE are DDL commands, whereas DELETE is a DML command. Therefore DELETE operations can be rolled back (undone), while DROP and TRUNCATE operations cannot be rolled back.
From Oracle 10g a table can be "undropped". Example:
SQL> FLASHBACK TABLE emp TO BEFORE DROP;
Flashback complete.
PS: DELETE will not free up used space within a table. This means that repeated DELETE commands will severely fragment the table and queries will have to navigate this "free space" in order to retrieve rows.
10. Truncate will not use the undo TBS, whereas a delete will.
What is High Water Mark in Oracle?
What is High Water Mark in Oracle?
Answer:
1. High water mark is the maximum amount of database blocks used so far by a segment. This mark cannot be reset by delete operations.
2. Delete Table operation won't reset HWM.
3. TRUNCATE will reset HWM.
4. The high water mark level is just a line separate the used blocks and free blocks.
The blocks above the HWM level is free blocks, they are ready to use.
The blocks below the HWM level is used blocks, they are already used.
I hope now you understand well. see the below example.
for example, if you delete some huge records from the database, that data will delete but the blocks are not ready to used, because that blocks are still below HWM level, so delete command never reset the HWM level,
At the same time you truncate the date, then the data will delete and that used blocks will goto above the HWM level, now its ready to used. now they consider has free blocks.
Explanation in Detail:
http://asktom.oracle.com/pls/asktomf?p=100:11:0::::P11_QUESTION_ID:492636200346818072
Answer:
1. High water mark is the maximum amount of database blocks used so far by a segment. This mark cannot be reset by delete operations.
2. Delete Table operation won't reset HWM.
3. TRUNCATE will reset HWM.
4. The high water mark level is just a line separate the used blocks and free blocks.
The blocks above the HWM level is free blocks, they are ready to use.
The blocks below the HWM level is used blocks, they are already used.
I hope now you understand well. see the below example.
for example, if you delete some huge records from the database, that data will delete but the blocks are not ready to used, because that blocks are still below HWM level, so delete command never reset the HWM level,
At the same time you truncate the date, then the data will delete and that used blocks will goto above the HWM level, now its ready to used. now they consider has free blocks.
Explanation in Detail:
http://asktom.oracle.com/pls/asktomf?p=100:11:0::::P11_QUESTION_ID:492636200346818072
Friday, September 05, 2008
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Oracle EBS integration with Oracle IDCS for SSO
Oracle EBS integration with Oracle IDCS for SSO Oracle EBS SSO? Why is it so important? Oracle E-Business Suite is a widely used application...
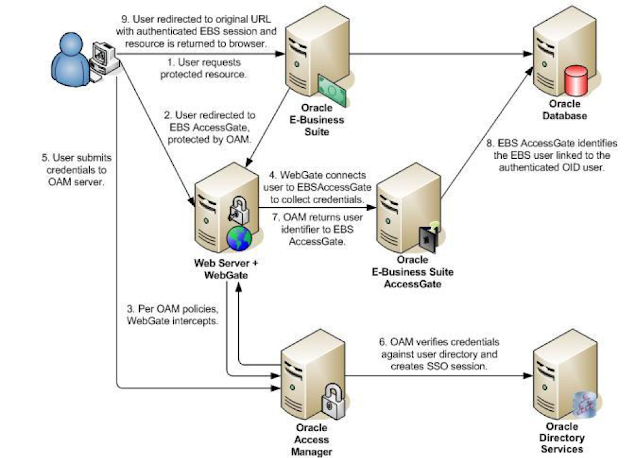
-
Enabling TLS in Oracle Apps R12.2 Here we would be looking at the detailed steps for Enabling TLS in Oracle Apps R12.2 Introduction: ...
-
Oracle EBS integration with Oracle IDCS for SSO Oracle EBS SSO? Why is it so important? Oracle E-Business Suite is a widely used application...
-
Apps password change routine in Release 12.2 E-Business Suite changed a little bit. We have now extra options to change password, as well ...

