1. What are .lct and .ldt files in Patch Directory?
Ans:
The patch metadata LDT files (also called datafiles) are FNDLOAD data files included in the top-level directory of all recent patches. The LDT files contain prerequisite patch information and a manifest of all files in the patch with their version numbers. The Patch Information Bundle metadata also include information about the relationships between patches, such as which minipacks are contained in the recommended.
LCT files (also called configfiles) are the configuration files which are used to download/upload data. Without configfiles, datafiles are useless.
2. If Ad worker fails during Ad patching, How many times by default adpatch automatically tries to resume the patching?
Ans:
Three Times
3. While trying to change one profile option at site level, the option is not editable mode? How to make it editable mode?
Ans:
Goto Application Developer -> Profiles -> Give Profile Options Names -> Check updatable
4. How do you check Compatibility of Oracle Applications with Any operating System?
Ans:
Metalink -> Certify Tab -> View Certification by platform
5. How do you check Latest CPU Patch for Oracle Server and Applications?
Ans:
Metalink -> Patches & Updates Tab
6. In RAC env, Each node contains How many IPs?
Ans:
Three
7. What are the tables updated when you apply application patch?
Ans:
ad_applied_patches and ad_bugs
8. Can you apply Opatch without inventory?
Ans:
No
9. If there is no inventory, How do you apply a opatch?
Ans:
Create inventory using runInstaller
10. What are the tables get created during Apps Patching?
Ans:
ad_deferred_jobs and fnd_installed_processes
11. Default environment variable to be set for Forms Config files?
Ans:
FORMS60_WEB_CONFIG_FILE
12. Profile option to determine which dbc file to use?
Ans:
Application Database ID
13. How do you hide apps password during adpatching?
Ans:
adpatch flags=hidepw
14. What is inter operability patch?
Ans:
OS compatibility patch, mostly applied during upgradation
15. How do you compile jsp files?
Ans:
Using adadmin or ojspCompile(perl -x $JTF_TOP/admin/scripts/ojspCompile.pl)
16. What is cache in Concurrent Managers Definition?
Ans:
No of concurrent requets that have to be cached from fnd_concurrent_requests while reading fnd_concurrent_requests
17. Types of profile options?
Ans:
1. Site level
2. User level
3. Responsibility Level
4. Server Level
5. Application Level
18. Opatch log file location ?
Ans:
$ORACLE_HOME/.patch_storage/patch_number/*.log
19. Different levels of SQL Tracing?
Ans:
Regular (Level 1 – standard/default level)
Level 4 (standard + binds)
Level 8 (standard + waits)
Level 12 (standard + binds and waits)
20. If you lost all redo logs files during DB is up and running? What will happen how do you recover it?
Ans:
DB will get crashed immediately
Solution;
1. You have to go for Incomplete Recovery
2. One way: Take previous backup, recover up to last archive and open the database
3. Second way: open the database in no mount state, create control file with rest logs and open the database with rest logs.
21. DB is up and running fine? you lost one data file? DB is in archive log mode? How do you recover it?
Ans:
1. If you have a backup of datafile, restore it and apply archives.
2. If you don't have backup of datafile, create datafile in database and apply archives.
22. How do you clone a context file or how do you change existing port pool?
Ans:
Using adclonectx.pl, you can clone next context file, during cloning you can give new port pool, and run autoconfig
23. How do you run autoconfig in test mode?
Ans:
adchkcfg.sh (AD_TOP/bin)
24. If you lost dbc file, How will you recover it?
Ans:
Using adgendbc($AD_TOP/bin) or run Autoconfig
Sharing real time knowledge,issues on Oracle Apps DBA and Oracle DBA
Showing posts with label Interview Questions. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Interview Questions. Show all posts
Saturday, April 18, 2009
Friday, January 16, 2009
Oracle Apps DBA Interview Questions Links
http://appsdba4u.blogspot.com/2007/08/oracle-apps-dba-interview-questions.html
http://appsdbablog.wordpress.com/2006/09/11/apps-dba-interview-questions
http://www.appsdbatraining.com/2011/03/17/oracle-apps-dba-interview-questions-vi/
http://onlineappsdba.com/index.php/category/intervi%20ewqs
http://searchoracle.techtarget.com/tip/0,289483,sid41_gci1111676,00.html
http://onlineappsdba.com/index.php/2007/09/30/oracle-apps-dba-interview-questions-install
http://www.vfreshersjobs.com/2011/11/oracle-apps-dba-11ir12-interview.html
http://appsdba.info/index.php?module=pagemaster&PAGE_user_op=view_page&PAGE_id=58&MMN_position=53:53
http://appsdbafaqs.blogspot.com
http://www.dbatutor.com/2011/01/oracle-application-dba-11i-interview.html
http://appsdbablog.wordpress.com/2006/09/11/apps-dba-interview-questions
http://www.appsdbatraining.com/2011/03/17/oracle-apps-dba-interview-questions-vi/
http://onlineappsdba.com/index.php/category/intervi%20ewqs
http://searchoracle.techtarget.com/tip/0,289483,sid41_gci1111676,00.html
http://onlineappsdba.com/index.php/2007/09/30/oracle-apps-dba-interview-questions-install
http://www.vfreshersjobs.com/2011/11/oracle-apps-dba-11ir12-interview.html
http://appsdba.info/index.php?module=pagemaster&PAGE_user_op=view_page&PAGE_id=58&MMN_position=53:53
http://appsdbafaqs.blogspot.com
http://www.dbatutor.com/2011/01/oracle-application-dba-11i-interview.html
Wednesday, January 14, 2009
parallelism in Oracle?
Complete about Oracle Parallelism?
Solution:
Following initialization parameters are required for parallelism setup in database.
PARALLEL_SERVER,
PARALLEL_SERVER_INSTANCES,
PARALLEL_MIN_SERVERS,
PARALLEL_MAX_SERVERS?
PARALLEL_THREADS_PER_CPU
Parallel Queries and Parallel jobs execution
1. Select query with parallelism example:
Select /*+ parallel (a,32) */ * from dba_segments a;
32 is degreee here(Numbers of parallel processes)
Gather statistics of a table using parallelism Example
exec FND_STATS.GATHER_TABLE_STATS (ownname => '&owner', tabname => '&table_name', percent => 20 ,degree => 30 , granularity => 'ALL', cascade => TRUE);
Comple objects in the database with parallelism Example
exec sys.utl_recomp.recomp_parallel(32);
Table used to know number of parallel processes running are
v$px_session - Standard
gv$px_session - For RAC
Solution:
Following initialization parameters are required for parallelism setup in database.
PARALLEL_SERVER,
PARALLEL_SERVER_INSTANCES,
PARALLEL_MIN_SERVERS,
PARALLEL_MAX_SERVERS?
PARALLEL_THREADS_PER_CPU
Parallel Queries and Parallel jobs execution
1. Select query with parallelism example:
Select /*+ parallel (a,32) */ * from dba_segments a;
32 is degreee here(Numbers of parallel processes)
Gather statistics of a table using parallelism Example
exec FND_STATS.GATHER_TABLE_STATS (ownname => '&owner', tabname => '&table_name', percent => 20 ,degree => 30 , granularity => 'ALL', cascade => TRUE);
Comple objects in the database with parallelism Example
exec sys.utl_recomp.recomp_parallel(32);
Table used to know number of parallel processes running are
v$px_session - Standard
gv$px_session - For RAC
Difference between DROP,Truncate and Delete in Oracle?
Difference between Truncate and Delete in Oracle?
Answer:
1.TRUNCATE is a DDL command and cannot be rolled back. All of the memory space is released back to the server.
2. DELETE is a DML command and can be rolled back.
3. TRUNCATE : You can't use WHERE clause and DELETE : You can use WHERE clause
4. Both commands accomplish identical tasks (removing all data from a table), but TRUNCATE is much faster.
5.Truncate: Drop all object's statistics and marks like High Water Mark, free extents and leave the object really empty with the first extent.Delete: You can keep object's statistics and all allocated space.
6. In case of TRUNCATE ,Trigger doesn't get fired.But in DML commands like DELETE .Trigger get fired.
7. Drop command will delete the entire row also the structure.But truncate will delete the contenets only not the strucure, so no need to give specifications for another table creation.
8. Drop command remove the table from data dictionary. This is the DDL statement. We can not recover the table before Oracle 10g. But Oracle 10g provide the command to recover it by using the command (FLASHBACK)
9. DROP and TRUNCATE are DDL commands, whereas DELETE is a DML command. Therefore DELETE operations can be rolled back (undone), while DROP and TRUNCATE operations cannot be rolled back.
From Oracle 10g a table can be "undropped". Example:
SQL> FLASHBACK TABLE emp TO BEFORE DROP;
Flashback complete.
PS: DELETE will not free up used space within a table. This means that repeated DELETE commands will severely fragment the table and queries will have to navigate this "free space" in order to retrieve rows.
10. Truncate will not use the undo TBS, whereas a delete will.
Answer:
1.TRUNCATE is a DDL command and cannot be rolled back. All of the memory space is released back to the server.
2. DELETE is a DML command and can be rolled back.
3. TRUNCATE : You can't use WHERE clause and DELETE : You can use WHERE clause
4. Both commands accomplish identical tasks (removing all data from a table), but TRUNCATE is much faster.
5.Truncate: Drop all object's statistics and marks like High Water Mark, free extents and leave the object really empty with the first extent.Delete: You can keep object's statistics and all allocated space.
6. In case of TRUNCATE ,Trigger doesn't get fired.But in DML commands like DELETE .Trigger get fired.
7. Drop command will delete the entire row also the structure.But truncate will delete the contenets only not the strucure, so no need to give specifications for another table creation.
8. Drop command remove the table from data dictionary. This is the DDL statement. We can not recover the table before Oracle 10g. But Oracle 10g provide the command to recover it by using the command (FLASHBACK)
9. DROP and TRUNCATE are DDL commands, whereas DELETE is a DML command. Therefore DELETE operations can be rolled back (undone), while DROP and TRUNCATE operations cannot be rolled back.
From Oracle 10g a table can be "undropped". Example:
SQL> FLASHBACK TABLE emp TO BEFORE DROP;
Flashback complete.
PS: DELETE will not free up used space within a table. This means that repeated DELETE commands will severely fragment the table and queries will have to navigate this "free space" in order to retrieve rows.
10. Truncate will not use the undo TBS, whereas a delete will.
What is High Water Mark in Oracle?
What is High Water Mark in Oracle?
Answer:
1. High water mark is the maximum amount of database blocks used so far by a segment. This mark cannot be reset by delete operations.
2. Delete Table operation won't reset HWM.
3. TRUNCATE will reset HWM.
4. The high water mark level is just a line separate the used blocks and free blocks.
The blocks above the HWM level is free blocks, they are ready to use.
The blocks below the HWM level is used blocks, they are already used.
I hope now you understand well. see the below example.
for example, if you delete some huge records from the database, that data will delete but the blocks are not ready to used, because that blocks are still below HWM level, so delete command never reset the HWM level,
At the same time you truncate the date, then the data will delete and that used blocks will goto above the HWM level, now its ready to used. now they consider has free blocks.
Explanation in Detail:
http://asktom.oracle.com/pls/asktomf?p=100:11:0::::P11_QUESTION_ID:492636200346818072
Answer:
1. High water mark is the maximum amount of database blocks used so far by a segment. This mark cannot be reset by delete operations.
2. Delete Table operation won't reset HWM.
3. TRUNCATE will reset HWM.
4. The high water mark level is just a line separate the used blocks and free blocks.
The blocks above the HWM level is free blocks, they are ready to use.
The blocks below the HWM level is used blocks, they are already used.
I hope now you understand well. see the below example.
for example, if you delete some huge records from the database, that data will delete but the blocks are not ready to used, because that blocks are still below HWM level, so delete command never reset the HWM level,
At the same time you truncate the date, then the data will delete and that used blocks will goto above the HWM level, now its ready to used. now they consider has free blocks.
Explanation in Detail:
http://asktom.oracle.com/pls/asktomf?p=100:11:0::::P11_QUESTION_ID:492636200346818072
Monday, September 08, 2008
Oracle Apps DBA Interview Questions
Oracle Apps DBA - Interview Questions
1. what is the utility to change the password of a dba schema in oracle apps? Ans: FNDCPASS
2. what are mandatory users in oracle apps?
Ans: applsys,applsyspub,apps
3. What simplay a oracle Architechture?
Ans: Desktop Tier, Application Tier, Database Tier 5. What are the components in the Application Tier?
Ans: Apache(http)
Jserver(jre)
Forms Server(f60srv)
Metric Server(d2ls)
Metric Client(d2lc)
Report Server(rwm60)
Concurrent Server(FNDLIBR)
Discoverer 6.What are main file systems in Oracle Apps?
Ans: APPL_TOP, COMMON_TOP,
DB_TOP,ORA_TOP 7. What are there in Desktop Tier?
Ans: Internet Browser, JInitiator 8. What is the location of JInitiator in the Desktop Tier?
Ans: c:\program files\oracle\Jinitiator 9. What is the location of client cache?
Ans: c:\documents and settngs\user\oracle jar Cache 10. What is the location of Server cache?
Ans: $COMMON_TOP/_pages
11. Which package will be used for the user validation by plsql agent?
Ans: oraclemypage
12. What are adadmin utilities? and Its location?
$AD_TOP/bin
Ans: 1.adadmin
2.adpatch
3.adsplice
4.adident
5.adrelink
6.adlicmgr
13.What are the location of JaVA Files?
Ans: JAVA_TOP and all PRODUCT_TOP/Java/Jar
14. What is the name of the xml file of Apps and its location?
Ans: Context Name.xml and $APPL_TOP/admin
15. what is the location of Apps environment file? and its name?
Ans: contextname.env and $APPL_TOP
16. In how many way Jar files are generated?
Ans: Normal and Force
17. Once Jar files are generated what files get effected?
Ans: All Product_top/java/jar files and Two files in JAVA_TOP they are appsborg.zip
appsborg2.zip
18. How do you see the files in zip file?
Ans: unzip -v
19.How do you generate jar files?
Ans: Using adadmin and option 5
20. How do you start the apps services?
Ans: $COMMON_TOP\admin\scripts\Contextname\adstrtal.sh apps/appspwd
21. What is the executable to generate jar files?
Ans: adjava
22. How do you relink a executable of a product
Ans: by relinking option in adadmin or adrelink
23. How do you relink AD product executable? and usage?
Ans: adrelink.sh and adrelink.sh force=y "ad adsplice"
24.When do you relinking?
Ans: 1. when you miss a executable file
2. When there is a problem with any executable file
3. When any product executable get currupted
25. What is DAD?
Ans: It is a file which stores apps passwords in hard coded format. i.e wdbsvr
26.How do you relink OS files and libraries?
Ans: using make command
27.What is compile scheman option in adadmin?
Ans: This option is used to compile/resolve the invalid objects
28. Where do you get the info about invalid objects?
Ans: from dba_objects where status=invalid
29.How do you compile an obect ?
Ans: alter object_ type objet _name compile. Eg: alter table fnd_nodes compile
30.How do you see the errors of a table or view?
Ans: select text from dba_errors where name='emp_view'
31. How do you see the errors in the db?
Ans: show error
32. How do you compile a schema?
Ans: using utlrp.sql (location is ?/rdbms/admin/) or
going adadmin, compile schema option
33. How do you know how many invalid objects are in specific schema?
Ans: select count(*) from dba_objects where status='INVALID' group by owner;
34. How do you know the package version?
Ans: select text from dba_source where name='package name' and type='PACKAGE BODY' and rownum<10>/rdbms/admin)
41. How do you load java class to databae?
Ans: loadjava
42. What are restart files? and its location?
Ans: These files contains the previouse session info about adadmin.. location is $APPL_TOP\admin\sid\restart\*.rf9
43.How do you validate apps schema?
Ans: To validate synonyms, missing sysnonyms and all grant. You can do it in adadmin. after validating it iwll produce
a report in the location $APPL_TOP\admin\sid\out\*.out
44. How do you enable maintainance mode?
Ans: using adadmin or running a script called "adsetmmd.sql ENABLE/DISABLE" (AD_TOP/patch/115/sql)
45.What is APPS_MRC Schema?
Ans: It is used for multi language support. To synchronize APPs schema and APPS_MRC
46. How to see the version of a script or form or report or etc?
Ans: grep Header adsetmmd.sql or adident Header adsetmmd.sql
strings -a GLXSTEA.fmx grep Header or adident Header GLXSTEA.fmx
47.What is the location of adadmin log?
Ans: $APPL_TOP\admin\sid\log
48. What are the oracle homes in Apps?
Ans: 8.0.6ORACLE_HOME(Dev 6i products) and IAS_ORACLE_HOME (Apache)
49. How do you configure you ipaddress at client side? and server side?
Ans: c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts and \etc\host
50. What is the location of Datbase server related scripts?
Ans: $ORACLE_HOME\appsutil\scripts\contextname
51. what is the utility to clean the concurrent manager?
Ans: @cmclean.sql ( You have download from metalink)
52. How do you stage the 11.5.10 Apps software?
Ans: using adautostg.pl
53. What is the location of the source files of forms?
Ans: AU_TOP/forms/US/
54. What is the executable to generate forms?
Ans: f60gen
1. what is the utility to change the password of a dba schema in oracle apps? Ans: FNDCPASS
2. what are mandatory users in oracle apps?
Ans: applsys,applsyspub,apps
3. What simplay a oracle Architechture?
Ans: Desktop Tier, Application Tier, Database Tier 5. What are the components in the Application Tier?
Ans: Apache(http)
Jserver(jre)
Forms Server(f60srv)
Metric Server(d2ls)
Metric Client(d2lc)
Report Server(rwm60)
Concurrent Server(FNDLIBR)
Discoverer 6.What are main file systems in Oracle Apps?
Ans: APPL_TOP, COMMON_TOP,
DB_TOP,ORA_TOP 7. What are there in Desktop Tier?
Ans: Internet Browser, JInitiator 8. What is the location of JInitiator in the Desktop Tier?
Ans: c:\program files\oracle\Jinitiator 9. What is the location of client cache?
Ans: c:\documents and settngs\user\oracle jar Cache 10. What is the location of Server cache?
Ans: $COMMON_TOP/_pages
11. Which package will be used for the user validation by plsql agent?
Ans: oraclemypage
12. What are adadmin utilities? and Its location?
$AD_TOP/bin
Ans: 1.adadmin
2.adpatch
3.adsplice
4.adident
5.adrelink
6.adlicmgr
13.What are the location of JaVA Files?
Ans: JAVA_TOP and all PRODUCT_TOP/Java/Jar
14. What is the name of the xml file of Apps and its location?
Ans: Context Name.xml and $APPL_TOP/admin
15. what is the location of Apps environment file? and its name?
Ans: contextname.env and $APPL_TOP
16. In how many way Jar files are generated?
Ans: Normal and Force
17. Once Jar files are generated what files get effected?
Ans: All Product_top/java/jar files and Two files in JAVA_TOP they are appsborg.zip
appsborg2.zip
18. How do you see the files in zip file?
Ans: unzip -v
19.How do you generate jar files?
Ans: Using adadmin and option 5
20. How do you start the apps services?
Ans: $COMMON_TOP\admin\scripts\Contextname\adstrtal.sh apps/appspwd
21. What is the executable to generate jar files?
Ans: adjava
22. How do you relink a executable of a product
Ans: by relinking option in adadmin or adrelink
23. How do you relink AD product executable? and usage?
Ans: adrelink.sh and adrelink.sh force=y "ad adsplice"
24.When do you relinking?
Ans: 1. when you miss a executable file
2. When there is a problem with any executable file
3. When any product executable get currupted
25. What is DAD?
Ans: It is a file which stores apps passwords in hard coded format. i.e wdbsvr
26.How do you relink OS files and libraries?
Ans: using make command
27.What is compile scheman option in adadmin?
Ans: This option is used to compile/resolve the invalid objects
28. Where do you get the info about invalid objects?
Ans: from dba_objects where status=invalid
29.How do you compile an obect ?
Ans: alter object_ type objet _name compile. Eg: alter table fnd_nodes compile
30.How do you see the errors of a table or view?
Ans: select text from dba_errors where name='emp_view'
31. How do you see the errors in the db?
Ans: show error
32. How do you compile a schema?
Ans: using utlrp.sql (location is ?/rdbms/admin/) or
going adadmin, compile schema option
33. How do you know how many invalid objects are in specific schema?
Ans: select count(*) from dba_objects where status='INVALID' group by owner;
34. How do you know the package version?
Ans: select text from dba_source where name='package name' and type='PACKAGE BODY' and rownum<10>/rdbms/admin)
41. How do you load java class to databae?
Ans: loadjava
42. What are restart files? and its location?
Ans: These files contains the previouse session info about adadmin.. location is $APPL_TOP\admin\sid\restart\*.rf9
43.How do you validate apps schema?
Ans: To validate synonyms, missing sysnonyms and all grant. You can do it in adadmin. after validating it iwll produce
a report in the location $APPL_TOP\admin\sid\out\*.out
44. How do you enable maintainance mode?
Ans: using adadmin or running a script called "adsetmmd.sql ENABLE/DISABLE" (AD_TOP/patch/115/sql)
45.What is APPS_MRC Schema?
Ans: It is used for multi language support. To synchronize APPs schema and APPS_MRC
46. How to see the version of a script or form or report or etc?
Ans: grep Header adsetmmd.sql or adident Header adsetmmd.sql
strings -a GLXSTEA.fmx grep Header or adident Header GLXSTEA.fmx
47.What is the location of adadmin log?
Ans: $APPL_TOP\admin\sid\log
48. What are the oracle homes in Apps?
Ans: 8.0.6ORACLE_HOME(Dev 6i products) and IAS_ORACLE_HOME (Apache)
49. How do you configure you ipaddress at client side? and server side?
Ans: c:\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts and \etc\host
50. What is the location of Datbase server related scripts?
Ans: $ORACLE_HOME\appsutil\scripts\contextname
51. what is the utility to clean the concurrent manager?
Ans: @cmclean.sql ( You have download from metalink)
52. How do you stage the 11.5.10 Apps software?
Ans: using adautostg.pl
53. What is the location of the source files of forms?
Ans: AU_TOP/forms/US/
54. What is the executable to generate forms?
Ans: f60gen
Wednesday, September 03, 2008
Oracle DBA -Performance Tuning Questions
Oracle DBA - Performance Tuning Interview Questions
1. What is Performance Tuning?
Ans: Making optimal use of system using existing resources called performace tuning.
2. Types of Tunings?
Ans: 1. CPU Tuning 2. Memory Tuning 3. IO Tuning 4. Application Tuning 5. Databse Tuning
3. What Mailny Database Tuning contains?
Ans: 1. Hit Ratios 2. Wait Events
3. What is an optimizer?
Ans: Optimizer is a mechanizm which will make the execution plan of an sql statement
4. Types of Optimizers?
Ans: 1. RBO(Rule Based Optimizer) 2. CBO(Cost Based Optimzer)
5. Which init parameter is used to make use of Optimizer?
Ans: optimizer_mode= rule----RBO cost---CBO choose--------First CBO otherwiser RBO
6. Which optimizer is the best one?
Ans: CBO
7. What are the pre requsited to make use of Optimizer?
Ans: 1. Set the optimizer mode 2. Collect the statistics of an object
8. How do you collect statistics of a table?
Ans: analyze table emp compute statistics or analyze table emp estimate statistics
9. What is the diff between compute and estimate?
Ans: If you use compute, The FTS will happen, if you use estimate just 10% of the table will be read
10. What wll happen if you set the optimizer_mode=choose?Ans: If the statistics of an object is available then CBO used. if not RBO will be used
11. Data Dictionay follows which optimzer mode?
Ans: RBO
12. How do you delete statistics of an object?
Ans: analyze table emp delete statistics
13. How do you collect statistics of a user/schema?
Ans: exec dbms_stats.gather_schema_stats(scott)
14. How do you see the statistics of a table?
Ans: select num_rows,blocks,empty_blocks from dba_tables where tab_name='emp'
15. What are chained rows?
Ans: These are rows, it spans in multiple blocks
16. How do you collect statistics of a user in Oracle Apps?
Ans: fnd_stats package
17. How do you create a execution plan and how do you see?Ans: 1. @?/rdbms/admin/utlxplan.sql --------- it creates a plan_table 2. explain set statement_id='1' for select * from emp; 3. @?/rdbms/admin/utlxpls.sql -------------it display the plan
18. How do you know what sql is currently being used by the session?
Ans: by goind v$sql and v$sql_area
19. What is a execution plan?
Ans: Its a road map how sql is being executed by oracle db?
20. How do you get the index of a table and on which column the index is?
Ans: dba_indexes and dba_ind_columns
21. Which init paramter you have to set to by pass parsing?
Ans: cursor_sharing=force
22. How do you know which session is running long jobs?
Ans: by going v$session_longops
23. How do you flush the shared pool?
Ans: alter system flush shared_pool
24. How do you get the info about FTS?
Ans: using v$sysstat
25. How do you increase the db cache?
Ans: alter table emp cache
26. Where do you get the info of library cache?
Ans: v$librarycache
27. How do you get the information of specific session?
Ans: v$mystat
28. How do you see the trace files?
Ans: using tkprof --- usage: tkprof allllle.trc llkld.txt
29. Types of hits?
Ans: Buffer hit and library hit
30. Types of wait events?
Ans: cpu time and direct path read
1. What is Performance Tuning?
Ans: Making optimal use of system using existing resources called performace tuning.
2. Types of Tunings?
Ans: 1. CPU Tuning 2. Memory Tuning 3. IO Tuning 4. Application Tuning 5. Databse Tuning
3. What Mailny Database Tuning contains?
Ans: 1. Hit Ratios 2. Wait Events
3. What is an optimizer?
Ans: Optimizer is a mechanizm which will make the execution plan of an sql statement
4. Types of Optimizers?
Ans: 1. RBO(Rule Based Optimizer) 2. CBO(Cost Based Optimzer)
5. Which init parameter is used to make use of Optimizer?
Ans: optimizer_mode= rule----RBO cost---CBO choose--------First CBO otherwiser RBO
6. Which optimizer is the best one?
Ans: CBO
7. What are the pre requsited to make use of Optimizer?
Ans: 1. Set the optimizer mode 2. Collect the statistics of an object
8. How do you collect statistics of a table?
Ans: analyze table emp compute statistics or analyze table emp estimate statistics
9. What is the diff between compute and estimate?
Ans: If you use compute, The FTS will happen, if you use estimate just 10% of the table will be read
10. What wll happen if you set the optimizer_mode=choose?Ans: If the statistics of an object is available then CBO used. if not RBO will be used
11. Data Dictionay follows which optimzer mode?
Ans: RBO
12. How do you delete statistics of an object?
Ans: analyze table emp delete statistics
13. How do you collect statistics of a user/schema?
Ans: exec dbms_stats.gather_schema_stats(scott)
14. How do you see the statistics of a table?
Ans: select num_rows,blocks,empty_blocks from dba_tables where tab_name='emp'
15. What are chained rows?
Ans: These are rows, it spans in multiple blocks
16. How do you collect statistics of a user in Oracle Apps?
Ans: fnd_stats package
17. How do you create a execution plan and how do you see?Ans: 1. @?/rdbms/admin/utlxplan.sql --------- it creates a plan_table 2. explain set statement_id='1' for select * from emp; 3. @?/rdbms/admin/utlxpls.sql -------------it display the plan
18. How do you know what sql is currently being used by the session?
Ans: by goind v$sql and v$sql_area
19. What is a execution plan?
Ans: Its a road map how sql is being executed by oracle db?
20. How do you get the index of a table and on which column the index is?
Ans: dba_indexes and dba_ind_columns
21. Which init paramter you have to set to by pass parsing?
Ans: cursor_sharing=force
22. How do you know which session is running long jobs?
Ans: by going v$session_longops
23. How do you flush the shared pool?
Ans: alter system flush shared_pool
24. How do you get the info about FTS?
Ans: using v$sysstat
25. How do you increase the db cache?
Ans: alter table emp cache
26. Where do you get the info of library cache?
Ans: v$librarycache
27. How do you get the information of specific session?
Ans: v$mystat
28. How do you see the trace files?
Ans: using tkprof --- usage: tkprof allllle.trc llkld.txt
29. Types of hits?
Ans: Buffer hit and library hit
30. Types of wait events?
Ans: cpu time and direct path read
Oracle DBA - Interview Questions
Oracle DBA - Interview Questions
1. How do you kill a session from the database?
Ans: alter system kill 'sid,serial#'
Usage : alter system kill '9,8' (Get the info from v$session
2. How do you know whether the process is Server Side Process?
Ans. By seeing the process in ps-ef as oracle+sid
eg: suppose the sid is prod, then the server process is refered as server side process and local=no
3. Daily Activities of a Oracle DBA?
Ans: 1. Check the Databse availability
2. Check the Listerner availability
3. check the alert log filie for errors
4. monitoring space availablilty in tablespaces
5. monitoring mount point (see capacity planning document)
6. Validate Database backup or Archive backup
7. Find objects which is going to reach max extents
8. Database Health check
9. CPU, Processor, Memory usage
4. Where do you get all hidden parameters ?
Ans: In the table x$ksppi
5. How do you see the names from that table?
Ans:select ksppinm,ksppdesc from x$ksppi where substr(ksppinm,1,1)='_'
6. How do increase the count of datafiles?
Ans: Generate the control file syntax from the existing control file and recreate the control file by changing the parameter MAXDATAFILES = yourdesired size
Procedure:
1. open the database
2. Generate the control file change the maxdatafiles
3. open the db in nomount
4. execute the syntax with noresetlogs
5. alter databse open
7. What is the init parameter to make use of profile?
Ans: resource_limits=true
8. How do you know whether the parameter is dynamic or static?
Ans: By going v$parameter and check the fields isses_modifiable and issys_modifible
9. What is the package and procedure name to conver dmt to lmt and vice versa?
Ans: exec dbms_space_admin.tablespace_migrate_from_local("gtb")
exec dbms_space_admin.tablespace_migrate_to_local("gtb1")
10. What is the use of nohup?
Ans: The execution of a specific task is performed in the server side with out any interupting
Usage : nohup cp -r * /tmp/. &
11. Where alert log is stored? What is the parameter?
Ans: in bdump. parameter is background_dump_dest
11. Where trace file are stored? What is the parameter?
Ans: in udump. parameter is user_dump_dest
12. Common Oracle Errors ……
1) ORA-01555 : Snapshot Too Old
2) ORA-01109 : Database Not Mounted
3) ORA-01507 : Database Not Open
4) ORA-01801 : Database already In startup mode.
5) ORA-600 : Internal error code for oracle program
Usage : oerr ORA 600
13. How do you enable traceing while you are in the database?
Ans : alter session set sql_trace=true;
14. If you want to enable tracing in remote system? what will u do?
Ans: exec dbms_system.SET_SQL_TRACE_IN_SESSION(9,3,TRUE);
15. Which role you grant to rman user while configuring rman user
Ans: recover_catalog_owner
16. Where do you get to know the version of your oracle software and what is your version?
Ans: from v$version(field is banner) and the version is 9.2.0.1.0
17. What is the parameters to set in the init.ora if you create db using OMF(Oracle Managed Files)?
Ans: db_create_file_dest=
db_create_online_log_dest_1=
18. What is a runaway session?
Ans: you killed a session in the database but it still remains in the os level and vice versa. Its called runaway session. If runaway session is there cpu consumes more usage.
19. How do you know whether the specific tablespace is in begin backup mode?
Ans: select status from v$backup. if it is active it means it is in begin backup mode
20. If you want to maintain one more archive destination which parameter you have to set ?
Ans:Its a dynamic parameter you have to set log_archive_duplex_dest=
Usage : alter system set log_archive_duplex_dest=
21. How do you know the create syntax of your function/procedure/index/synonym ?
Ans: using function dbms_metadata.get_ddl(object type,object name,owner)
22. What is the password you have to set in the init.ora to enable remote login ?
Ans: remote_login_password_file=exclusive
23.How do u set crontab to delete 5 days old trace files at daily 10'0 clock?
Ans: crontab -e
0 10 * * * /usr/bin/find /u001/admin/udump -name "*.trc" -mtime +5 -exec rm -rf {} \;
save and exit (wq!)
24.How do u know when system was last booted?
Ans: 3 ways 1.uptime cmd
2.top
3.who -b
4.w
24.How do u know load on system?
Ans: 1.w
2.top
25. How do you know when the process is started
Ans : Using ps -ef grep process name
26. Tell me the location of Unix/Solaris log messages stored?
Ans:/var/log/messages(Unix)
/var/adm/messages (solaris)
27.How do you take backup of a controlfile?
Ans: alter database backup controlfille to destination (Database should be open)
file will be save in the your destination
28. What is the parameter to set the user trace enabiling?
Ans: sql_trace = true
29. How do you know whether archive log mode is enable or not?
Ans: issue command 'archive log list' at sqlplus prompt
30. Where do you get the information of quotas?
Ans: dba_ts_quotas view
31. How do you know how much archives are generated ?
Ans: using the view v$log_history
32. What is a stale?
Ans: The redolog file which has not been used yet
33. How do you read the binary file?
Ans: using strings -a
usage : strings -a filename
34.How do you read control file?
Ans: using command tkprof
Usage: tkprof contrl.ctl ctrol2.txt
35. How do you send the data to tape?
Ans: using 1. tar -cvf or 2. cpio
36. How do you connect to db and startup and shutdown the db without having dba group?
Ans: using remote_login_passwordfile
37. When will you take Cold back up especially?
Ans: during upgradation and migration
38. How do you enable/disable debugging mode in unix?
Ans: set -x and set +x
39. How do you get the create syntax of a table or index or function or procedure?
Ans: select dbms_metadata.get_ddl('TABLE','EMP','SCOTT') from dual;
40. How do you replace a string in vi editor?
Ans: %s/name/newname
41. When ckpt occurs?
Ans: 1. for every 3 seconds
2. when 1/3rd of DB buffer fills
3. when log swtich occurs
4. when databse shuts down
42. In which file oracle inventory information is available?
Ans : /etc/oraInst.loc
42. Where all oracle homes and oracle sid information available?
Ans: /etc/oratab
43. What is the environment variable to set the location of the listener.ora
Ans: TNS_ADMIN
44. How do you know whether listener is running or not
Ans: ps -ef grep tns
45. What are the two steps involved in instace recovery?
Ans: 1. Roll forward (redofiles data to datafiles)
2. Roll backward (undo files to datafiles).
46. If you delete the alert log fle what will happen?
Ans: New alert log will be created automatically
57. How do you create a table in another tablespace name?
Ans: create table xyz (a number) tablespace system
58. What are the modes/options in incomplete recovery?
Ans: cancel based, change based, time based
59. How do you create an alias?
Ans: alias bdump='cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin'
60. Types of trace files?
Ans: 1. trace files generated by database (bdump)
2. trace files generated by user(udump)
61. How do you find the files whose are more than 500k?
Ans : fnd . -name "*" -size +500k
62. Where do you configure your hostname in linux?
Ans: vi /etc/hosts
63. What are the types of segments?
Ans: Data Segment,Undo Segment,Temporary segment,Index Segment
64. What is a synonym and different types of synonyms?
Ans: A synonym is an alias for a table,view, sequence or program unit.
1. Public synonym
2. private synonym
65. What are mandatory background processes in Oracle Database?
Ans: smon,pmon,ckpt,dbwr,lgwr
66. How do you make your redolog group inactive?
Ans: alter system switch logfile;
67. How do you drop a tablespace?
Ans: drop tablespace ts1 including contents and datafiles;
68. What is the parameter allows you to create max no. of groups?
Ans: maxlogfiles=
69. What is the paramter allows to create max no. of members in a group?
Ans: maxlognumbers=
70. What Controlfile contains?
Ans: Database name
Database creation time stamp
Address of datafiles and redolog files
Check point information
SCN information
71. What are the init parameters you have to set to make use of undo management?
Ans: undo_tablespace= undotbs1
undo_management= auto
undo_retention= time in minutes
comment rollback_segment
73. How do you enable monitoring of a table?
Ans: alter table tablename monitoring
74. How do you disable monitoring of a table?
Ans: alter table tablename no monitoring
75. How do you check the status of the table whether monitoring or not?
Ans: select table_name, monitoring from dba_table where owner='scott;
76. In which table records of monitoirg will be stored?
Ans: dba_tab_modificaitons
77. How do you get you demo files get created in your user?
Ans: ?/sqlplus/demo/demobld.sql execute this script on which user you want
78. What is netstat? and its Usage?
Ans: it is a utility to know the port numbers availability. Usage: netstat -na grep port number
79.How do you make use of stats pack?
Ans: 1. spcreate.sql (?/rdbms/admin/) -- to create statspack
2. execute statspack.snap -- to collect datbase snaps
3. spreport.sql-- to generate reports(in your current directory)
4. spauto.sql----to schedule a job
5. sppurge.sql---to delete statistics
6. spdrop.sql----to drop the statistics
1. How do you kill a session from the database?
Ans: alter system kill 'sid,serial#'
Usage : alter system kill '9,8' (Get the info from v$session
2. How do you know whether the process is Server Side Process?
Ans. By seeing the process in ps-ef as oracle+sid
eg: suppose the sid is prod, then the server process is refered as server side process and local=no
3. Daily Activities of a Oracle DBA?
Ans: 1. Check the Databse availability
2. Check the Listerner availability
3. check the alert log filie for errors
4. monitoring space availablilty in tablespaces
5. monitoring mount point (see capacity planning document)
6. Validate Database backup or Archive backup
7. Find objects which is going to reach max extents
8. Database Health check
9. CPU, Processor, Memory usage
4. Where do you get all hidden parameters ?
Ans: In the table x$ksppi
5. How do you see the names from that table?
Ans:select ksppinm,ksppdesc from x$ksppi where substr(ksppinm,1,1)='_'
6. How do increase the count of datafiles?
Ans: Generate the control file syntax from the existing control file and recreate the control file by changing the parameter MAXDATAFILES = yourdesired size
Procedure:
1. open the database
2. Generate the control file change the maxdatafiles
3. open the db in nomount
4. execute the syntax with noresetlogs
5. alter databse open
7. What is the init parameter to make use of profile?
Ans: resource_limits=true
8. How do you know whether the parameter is dynamic or static?
Ans: By going v$parameter and check the fields isses_modifiable and issys_modifible
9. What is the package and procedure name to conver dmt to lmt and vice versa?
Ans: exec dbms_space_admin.tablespace_migrate_from_local("gtb")
exec dbms_space_admin.tablespace_migrate_to_local("gtb1")
10. What is the use of nohup?
Ans: The execution of a specific task is performed in the server side with out any interupting
Usage : nohup cp -r * /tmp/. &
11. Where alert log is stored? What is the parameter?
Ans: in bdump. parameter is background_dump_dest
11. Where trace file are stored? What is the parameter?
Ans: in udump. parameter is user_dump_dest
12. Common Oracle Errors ……
1) ORA-01555 : Snapshot Too Old
2) ORA-01109 : Database Not Mounted
3) ORA-01507 : Database Not Open
4) ORA-01801 : Database already In startup mode.
5) ORA-600 : Internal error code for oracle program
Usage : oerr ORA 600
13. How do you enable traceing while you are in the database?
Ans : alter session set sql_trace=true;
14. If you want to enable tracing in remote system? what will u do?
Ans: exec dbms_system.SET_SQL_TRACE_IN_SESSION(9,3,TRUE);
15. Which role you grant to rman user while configuring rman user
Ans: recover_catalog_owner
16. Where do you get to know the version of your oracle software and what is your version?
Ans: from v$version(field is banner) and the version is 9.2.0.1.0
17. What is the parameters to set in the init.ora if you create db using OMF(Oracle Managed Files)?
Ans: db_create_file_dest=
db_create_online_log_dest_1=
18. What is a runaway session?
Ans: you killed a session in the database but it still remains in the os level and vice versa. Its called runaway session. If runaway session is there cpu consumes more usage.
19. How do you know whether the specific tablespace is in begin backup mode?
Ans: select status from v$backup. if it is active it means it is in begin backup mode
20. If you want to maintain one more archive destination which parameter you have to set ?
Ans:Its a dynamic parameter you have to set log_archive_duplex_dest=
Usage : alter system set log_archive_duplex_dest=
21. How do you know the create syntax of your function/procedure/index/synonym ?
Ans: using function dbms_metadata.get_ddl(object type,object name,owner)
22. What is the password you have to set in the init.ora to enable remote login ?
Ans: remote_login_password_file=exclusive
23.How do u set crontab to delete 5 days old trace files at daily 10'0 clock?
Ans: crontab -e
0 10 * * * /usr/bin/find /u001/admin/udump -name "*.trc" -mtime +5 -exec rm -rf {} \;
save and exit (wq!)
24.How do u know when system was last booted?
Ans: 3 ways 1.uptime cmd
2.top
3.who -b
4.w
24.How do u know load on system?
Ans: 1.w
2.top
25. How do you know when the process is started
Ans : Using ps -ef grep process name
26. Tell me the location of Unix/Solaris log messages stored?
Ans:/var/log/messages(Unix)
/var/adm/messages (solaris)
27.How do you take backup of a controlfile?
Ans: alter database backup controlfille to destination (Database should be open)
file will be save in the your destination
28. What is the parameter to set the user trace enabiling?
Ans: sql_trace = true
29. How do you know whether archive log mode is enable or not?
Ans: issue command 'archive log list' at sqlplus prompt
30. Where do you get the information of quotas?
Ans: dba_ts_quotas view
31. How do you know how much archives are generated ?
Ans: using the view v$log_history
32. What is a stale?
Ans: The redolog file which has not been used yet
33. How do you read the binary file?
Ans: using strings -a
usage : strings -a filename
34.How do you read control file?
Ans: using command tkprof
Usage: tkprof contrl.ctl ctrol2.txt
35. How do you send the data to tape?
Ans: using 1. tar -cvf or 2. cpio
36. How do you connect to db and startup and shutdown the db without having dba group?
Ans: using remote_login_passwordfile
37. When will you take Cold back up especially?
Ans: during upgradation and migration
38. How do you enable/disable debugging mode in unix?
Ans: set -x and set +x
39. How do you get the create syntax of a table or index or function or procedure?
Ans: select dbms_metadata.get_ddl('TABLE','EMP','SCOTT') from dual;
40. How do you replace a string in vi editor?
Ans: %s/name/newname
41. When ckpt occurs?
Ans: 1. for every 3 seconds
2. when 1/3rd of DB buffer fills
3. when log swtich occurs
4. when databse shuts down
42. In which file oracle inventory information is available?
Ans : /etc/oraInst.loc
42. Where all oracle homes and oracle sid information available?
Ans: /etc/oratab
43. What is the environment variable to set the location of the listener.ora
Ans: TNS_ADMIN
44. How do you know whether listener is running or not
Ans: ps -ef grep tns
45. What are the two steps involved in instace recovery?
Ans: 1. Roll forward (redofiles data to datafiles)
2. Roll backward (undo files to datafiles).
46. If you delete the alert log fle what will happen?
Ans: New alert log will be created automatically
57. How do you create a table in another tablespace name?
Ans: create table xyz (a number) tablespace system
58. What are the modes/options in incomplete recovery?
Ans: cancel based, change based, time based
59. How do you create an alias?
Ans: alias bdump='cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin'
60. Types of trace files?
Ans: 1. trace files generated by database (bdump)
2. trace files generated by user(udump)
61. How do you find the files whose are more than 500k?
Ans : fnd . -name "*" -size +500k
62. Where do you configure your hostname in linux?
Ans: vi /etc/hosts
63. What are the types of segments?
Ans: Data Segment,Undo Segment,Temporary segment,Index Segment
64. What is a synonym and different types of synonyms?
Ans: A synonym is an alias for a table,view, sequence or program unit.
1. Public synonym
2. private synonym
65. What are mandatory background processes in Oracle Database?
Ans: smon,pmon,ckpt,dbwr,lgwr
66. How do you make your redolog group inactive?
Ans: alter system switch logfile;
67. How do you drop a tablespace?
Ans: drop tablespace ts1 including contents and datafiles;
68. What is the parameter allows you to create max no. of groups?
Ans: maxlogfiles=
69. What is the paramter allows to create max no. of members in a group?
Ans: maxlognumbers=
70. What Controlfile contains?
Ans: Database name
Database creation time stamp
Address of datafiles and redolog files
Check point information
SCN information
71. What are the init parameters you have to set to make use of undo management?
Ans: undo_tablespace= undotbs1
undo_management= auto
undo_retention= time in minutes
comment rollback_segment
73. How do you enable monitoring of a table?
Ans: alter table tablename monitoring
74. How do you disable monitoring of a table?
Ans: alter table tablename no monitoring
75. How do you check the status of the table whether monitoring or not?
Ans: select table_name, monitoring from dba_table where owner='scott;
76. In which table records of monitoirg will be stored?
Ans: dba_tab_modificaitons
77. How do you get you demo files get created in your user?
Ans: ?/sqlplus/demo/demobld.sql execute this script on which user you want
78. What is netstat? and its Usage?
Ans: it is a utility to know the port numbers availability. Usage: netstat -na grep port number
79.How do you make use of stats pack?
Ans: 1. spcreate.sql (?/rdbms/admin/) -- to create statspack
2. execute statspack.snap -- to collect datbase snaps
3. spreport.sql-- to generate reports(in your current directory)
4. spauto.sql----to schedule a job
5. sppurge.sql---to delete statistics
6. spdrop.sql----to drop the statistics
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Oracle EBS integration with Oracle IDCS for SSO
Oracle EBS integration with Oracle IDCS for SSO Oracle EBS SSO? Why is it so important? Oracle E-Business Suite is a widely used application...
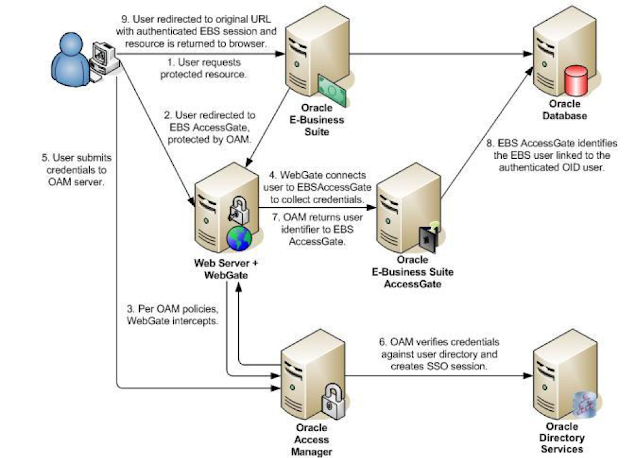
-
Enabling TLS in Oracle Apps R12.2 Here we would be looking at the detailed steps for Enabling TLS in Oracle Apps R12.2 Introduction: ...
-
Oracle EBS integration with Oracle IDCS for SSO Oracle EBS SSO? Why is it so important? Oracle E-Business Suite is a widely used application...
-
Apps password change routine in Release 12.2 E-Business Suite changed a little bit. We have now extra options to change password, as well ...

